How to Choose the Right Ventilator: Key Factors for Clinical & Home Use
Selecting a suitable ventilator requires balancing patient needs, clinical settings, and technical specifications. From ICU critical care to home respiratory support, understanding device types, gas requirements, and patient-specific parameters is crucial for safe and effective ventilation.
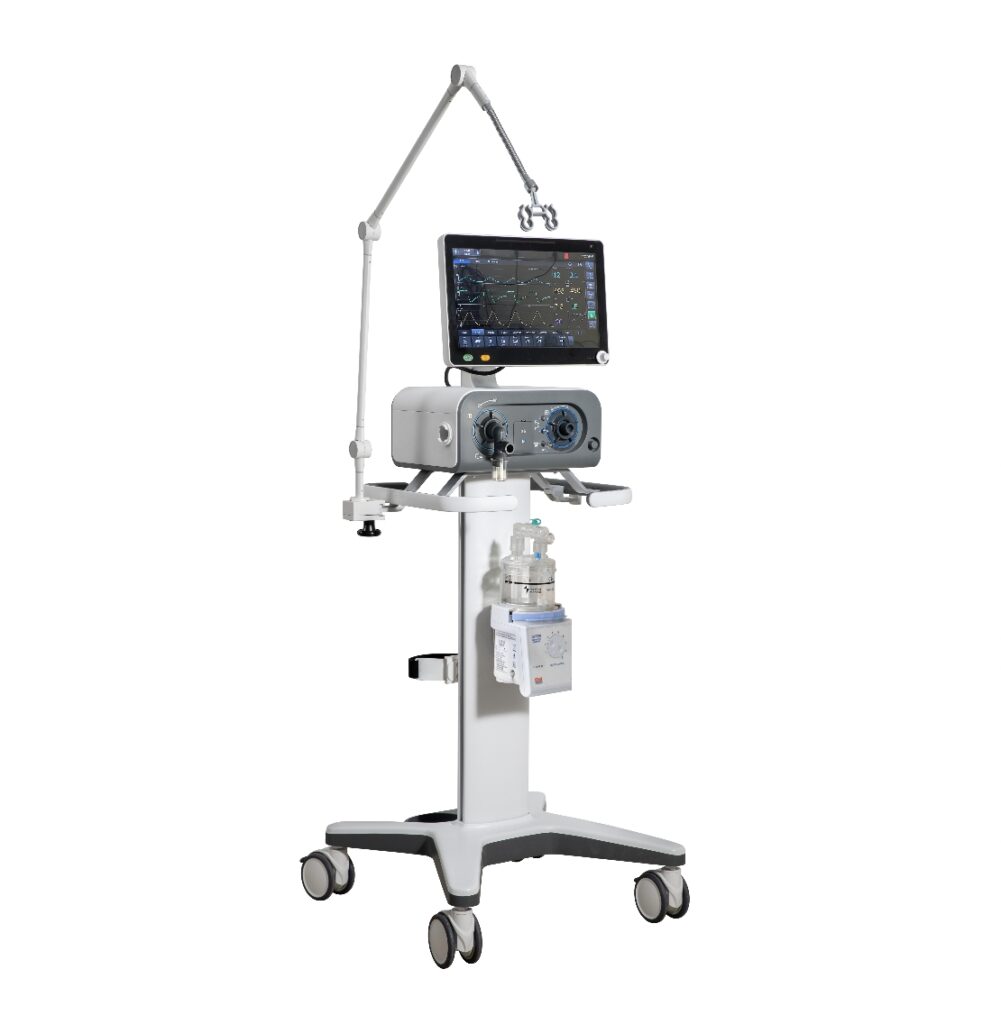
Ventilators fall into three primary categories based on use cases. ICU ventilators (e.g SM-VG03 SM-VG09,SM-VG70 ,SM-VG6) offer advanced modes like A/C-VCV, BIPAP, and APRV, supporting adults, pediatrics, and neonates. They excel in critical care, handling complex respiratory failures with precise parameter adjustment. Home care ventilators are compact, portable, and designed for chronic conditions like COPD, often using non-invasive interfaces (NIV). Transport ventilators( e.g SM-510S)prioritize mobility, operating on batteries for emergency transfers or ambulance use.
Gas supply systems are a defining factor: Most ICU and transport models require a compressor (blower-driven) to deliver ambient air, paired with an oxygen source (50-100% O₂). Home ventilators may use built-in compressors or rely on external oxygen cylinders (280-600 kPa supply pressure). For high-dependency care, integrated gas mixing systems ensure stable O₂ concentrations, while low-pressure alerts prevent supply failures.
Tidal volume (TV) is patient-specific, with neonates requiring meticulous calibration by weight Devices like the SM- V6 (5-2000 mL TV range and with optional to 2ml if you need) accommodate all age groups with adjustable settings. While most are starting from 20ml.
In summary, match the ventilator to the setting: ICU models for complex care, portable units for home/transport, and specialized designs for neonates. Verify gas system compatibility (compressor requirement, oxygen supply), and calibrate tidal volume to patient weight—especially for fragile neonatal populations. By aligning technical features with clinical needs, you ensure optimal respiratory support and patient outcomes.